Internal combustion engines have revolutionized the way we travel. They are found in everything from automobiles to helicopters, boats and some forms of public transportation. Understanding how they work can make you more knowledgeable about the world around you and help you maintain these important machines.
Read more: Everything You Need to Know About Modern Internal Combustion EnginesTypes of Internal Combustion Engines
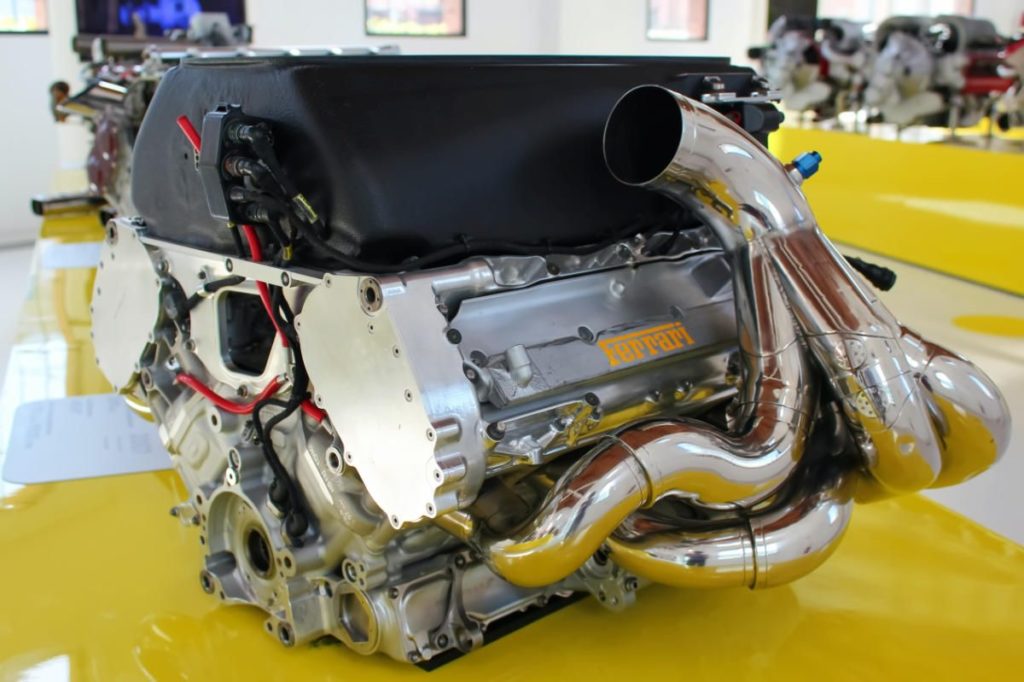

There are many different types of internal combustion engines used today. Automobiles have spark-ignition engines that use gasoline and require a spark plug to ignite the fuel. Diesel engines have no spark plugs and instead rely on heat produced by burning fossil fuels. Jet engines are used in aircraft to produce thrust.
Gasoline is an explosive liquid and when it is burned, it produces hot gases which are used to power the engine. The temperature of gasoline burning ranges from 1,000 Celsius in a spark-ignition engine to 1,650 Celsius in a diesel engine. These temperatures are much higher than what can be produced by fossil fuels alone. This is why most engines have heaters that help increase the temperature of the air entering the combustion chamber.
Parts of an Internal Combustion Engine
Inside an engine, there are three main parts: the compressor, the combustion chamber, and the expander. The compressor draws in air and sends it through a heater, which increases its temperature substantially. Next, the hot air is sent through a fuel injector where gasoline is sprayed into the stream.
The now-contaminated air then passes through the combustion chamber where a piston is at work creating a series of explosions that drive a shaft, producing power. This process requires high temperatures and pressures which can only be maintained by using sturdy metal alloys in the compressor and expander turbines.
The expander turbine is typically made up of two sets of blades. One set that rotates with the engine and one fixed set. The moving blades draw in hot gas from the combustion chamber, which increases their power. The fixed blades act as a fan, sending the hot gases out into the atmosphere. This creates thrust that can be used to propel an airplane or boat forward.
The compressor is powered by an engine and the expander is driven by a propeller or helicopter rotor. In automobiles and some aircraft, these two parts are combined into one unit called a turbine. Turbines have many uses in industry and are also found in everything from power plants and oil rigs to ocean-going vessels.
The compressor and expander turbines in an internal combustion engine are made up of a series of metal blades that rotate at very high speeds. These rotating parts require lubrication to move freely without wearing out. Oil is used for this purpose, but it must be cooled in order to prevent damage from excessive heat. Most modern engines have an oil cooler incorporated into their design so that they can continue functioning properly under all conditions.
Vehicles are also equipped with cylinder heads, which are connected to the engine block using a car gasket. The car gasket is a flexible seal that allows the engine to move freely while keeping the oil inside. When an automobile’s head gasket starts leaking, it is time for a replacement. This can save you from having to replace the entire engine in the future.
The cylinder head holds the valves that admit air and fuel into the combustion chamber. The camshaft is installed in the valve train to open and close these valves at precise times, which creates a series of explosions that drive the shafts and gears of an engine.
Exhaust Systems
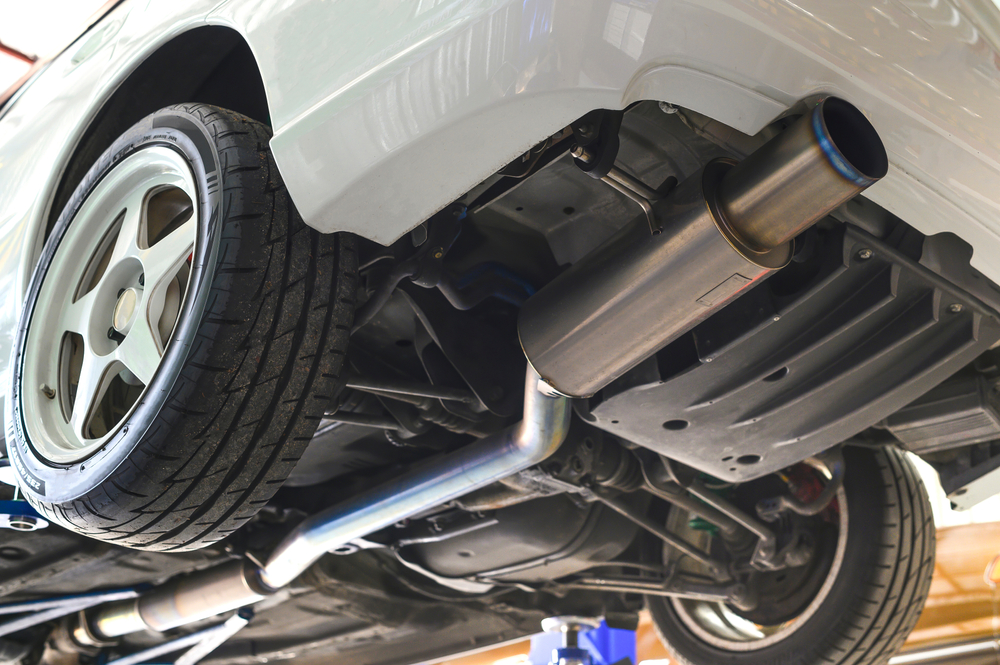

The exhaust system is also part of the vehicle’s combustion system and must be maintained regularly. It consists of several parts including mufflers and catalytic converters that reduce emissions by changing them into less harmful substances. In order for an engine to run, it must have fuel and air. Engines require some type of lubrication and a coolant system that keeps them operating at safe temperatures.
When an engine is idling, the piston moves back and forth in its bore with little force being applied to the shafts and gears. This allows time for the cooling systems to cool down after being heated by high-speed operation. The cylinder head also provides additional support to the block when idle.
Final Word
Now that you have a general idea of what parts comprise the modern internal combustion engine and how it works, you’ll have an easier time understanding your automobile’s manual when it comes time for maintenance and repairs. You’ll also have a better understanding of the automotive industry as a whole and be able to appreciate why some cars are more fuel efficient than others.